
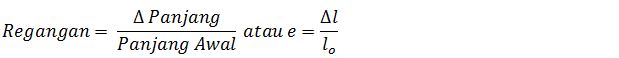
In this work Young modulus and Poisson ratio were found for sintered copper using circular plate torsial vibrations method So, finally we are left with three collision parameters e, et, and which are typical for the type of particle to be modeled. More on this point is given in the Section III.B.7 on efficiency issues. The values for kn and k, are thus mainly determined by computational efficiency and not by the material properties. In principle, kn and k, are related to the Young modulus and Poisson ratio of the solid material however, in practice their value must be chosen much smaller, otherwise the time step of the integration needs to become unpractically small. The contact force between two particles is now determined by only five parameters normal and tangential spring stiffness kn and kt, the coefficient of normal and tangential restitution e and et, and the friction coefficient /if. (3.57) and from the transformation equation for s j j. The numerical value of Young s modulus for each specified direction may be calculated from Eq.
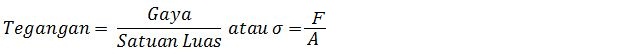
The endpoints of these radius vectors define the so called elasticity surface of the given crystal. To visualize the elastic properties of crystals it is common to draw a polar diagram with radius vectors of length equal to E (that is the reciprocal of Yj j) in all directions. In analogy to isotropic bodies we define Young s modulus in the direction considered here by the ratio of

Let us assume in addition that with respect to this primed coordinate system there is only one component of stress, namely T Let us choose the direction for which we wish to determine Young s modulus E as the x l axis of a coordinate system rotated with respect to the crystal coordinate system. Because of the anisotropy of crystals it is evident that this will always be possible only for one or two specified directions. We now turn briefly to the question to what extent it might make sense to deflne these quantities also for crystals. It is also quite generally known that these quantities are related by These quantities are of ubiquitous use in engineering. The elasticity of isotropic materials is usually described by Young s modulus E, the Poisson ratio v and by the shear modulus G.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
